In Azure if you have two or more SQL Databases and you want to perform a query across them, you might come across the following error:
Reference to database and/or server name in '[database table]' is not supported in this version of SQL Server.
In order to perform cross database queries among SQL Azure databases you need to use the elastic database query feature.
What is the Elastic Database Query Feature?
The elastic database query feature enables you to run a Transact-SQL query that spans multiple databases in Azure SQL Database (SQLDB). It allows you to perform cross-database queries to access remote tables, and to connect Microsoft and third party tools (Excel, PowerBI, Tableau, etc.) to query across data tiers with multiple databases. Using this feature, you can scale out queries to large data tiers in SQL Database and visualize the results in business intelligence (BI) reports.
Why use Elastic Database Queries?
- Using the elastic database query you can query across SQL Azure databases completely in T-SQL. This allows read-only querying of remote databases, and provides a way for current on-premises SQL Server customers to migrate applications linking servers between on-premises and SQL Azure environments.
- Elastic query is available on standard tier, but in big databases your query execution may be slow.
- You can execute stored procedures or remote functions using sp_execute _remote.
- External tables with elastic query can now refer to remote tables with a different schema or table name.
Common Topologies
The goal of using cross database queries is to facilitate querying scenarios where multiple databases contribute rows into a single overall result. Customer scenarios for elastic query are characterized by the following topologies:
Vertical partitioning – Cross-database queries
An elastic query can be used to make data located in an SQL database available to other SQL databases. This allows queries from one database to refer to tables in any other remote SQL database.
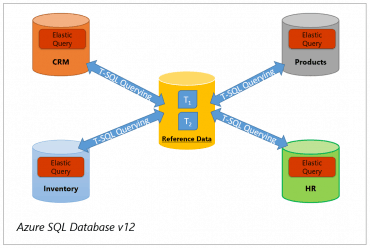
Horizontal Partitioning – Sharding
For horizontal partitioning, to perform reporting tasks over a sharded data tier, an elastic database shard map is required to represent the databases of the data tier.
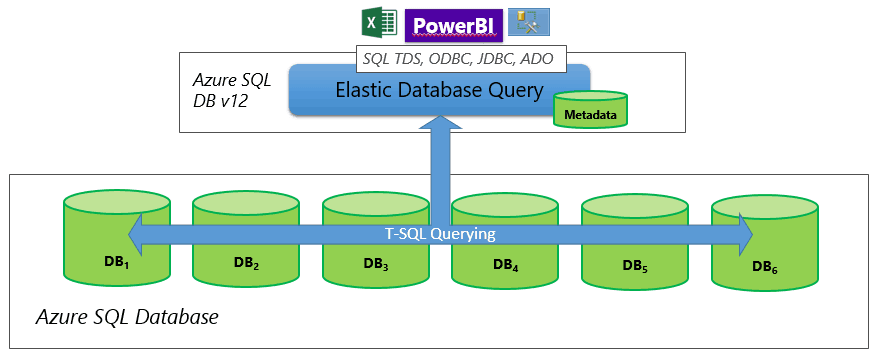
For more info on the two topologies, you may read this article.
Implementing elastic database queries
Let’s assume that we have created two databases in Azure, DB1 and DB2, with two tables in each respective database.
DB1 has Db1Table table:
CREATE TABLE DB1.dbo.Db1Table ( ID int IDENTITY(1, 1) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, CustomerId INT, CustomerName NVARCHAR(50) ); INSERT INTO DB1.dbo.Db1Table(CustomerId, CustomerName) VALUES ( 1, 'aaaaaaa' ), ( 2, 'bbbbbbb' ), ( 3, 'ccccccc' ), ( 4, 'ddddddd' ), ( 5, 'eeeeeee' );
DB2 has Db2Table table:
CREATE TABLE DB2.dbo.Db2Table ( ID int IDENTITY(1, 1) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, CustomerId INT, Country NVARCHAR(50) ); INSERT INTO DB2.dbo.Db2Table(CustomerId, Country) VALUES ( 1, 'United States' ), ( 3, 'Greece' ), ( 4, 'France' ), ( 5, 'Germany' ), ( 6, 'Ireland' );
If we want to fetch customers whose country is Greece then we could do the following query:
SELECT db1.CustomerId, db1.CustomerName FROM DB1.dbo.Db1Table db1 INNER JOIN DB2.dbo.Db2Table db2 ON db1.CustomerId = db2.CustomerId WHERE db2.Country = 'Greece';
but instead of returning customerId 3 we get the following error:
Reference to database and/or server name in 'DB2.dbo.Db2Table' is not supported in this version of SQL Server.
In order to be able to perform a cross database query we need to perform the following steps:
Step1: Create Master Key
The database master key is a symmetric key used to protect the private keys of certificates and asymmetric keys that are present in the database. More info here.
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = '<password>'; -- Example -- CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = '3wbASg68un@q'
Step 2: Create Database Scoped Credential “my_credential”
A database credential is not mapped to a server login or database user. The credential is used by the database to access the external location anytime the database is performing an operation that requires access.
CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL <credential_name> WITH IDENTITY = '<user>', SECRET = '<secret>'; -- Example -- CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL my_credential WITH IDENTITY = 'dbuser', SECRET = '9Pfwbg68un@q';
- credential_name
Specifies the name of the database scoped credential being created. credential_name cannot start with the number (#) sign. System credentials start with ##. - IDENTITY =’identity_name‘
Specifies the name of the account to be used when connecting outside the server.
- SECRET =’secret‘
Specifies the secret required for outgoing authentication.
Step 3: Create External Data Source “my_datasource” of type RDBMS
This instruction creates an external data source for use in Elastic Database queries. For RDBMS, it specifies the logical server name of the remote database in Azure SQL Database.
-- (only on Azure SQL Database v12 or later) CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE <data_source_name> WITH ( TYPE=RDBMS, LOCATION='<server_name>.database.secure.windows.net', DATABASE_NAME='<remote_database_name>', CREDENTIAL = <sql_credential> ); -- Example -- CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE my_datasource WITH ( TYPE=RDBMS, LOCATION='ppolsql.database.secure.windows.net', DATABASE_NAME='DB2', CREDENTIAL = my_credential );
- data_source_name
Specifies the user-defined name for the data source. The name must be unique within the database in Azure SQL Database. - TYPE = [ HADOOP | SHARD_MAP_MANAGER | RDBMS ]
Use RDBMS with external data sources for cross-database queries with Elastic Database query on Azure SQL Database. - LOCATION = <location_path>
specifies the logical server name of the remote database in Azure SQL Database.
- DATABASE_NAME = ‘remote_database_name’
The name of the remote database (for RDBMS). - CREDENTIAL = credential_name
Specifies a database-scoped credential for authenticating to the external data source.
Step 4: Create External Table “mytable”
This instruction creates an external table for Elastic Database query.
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [ database_name . [ schema_name ] . | schema_name. ] table_name
( <column_definition> [ ,...n ] )
WITH (
DATA_SOURCE = <data_source_name>
);
-- Example --
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [dbo].[Db2Table] (
[ID] int NOT NULL,
[CustomerId] INT,
[Country] NVARCHAR(50)
) WITH ( DATA_SOURCE = my_datasource )
- database_name . [ schema_name ] . | schema_name. ] table_name
The one to three-part name of the table to create. For an external table, only the table metadata is stored in SQL along with basic statistics about the file and/or folder referenced in Hadoop or Azure blob storage. No actual data is moved or stored in SQL Server. - <column_definition> [ ,…n ]
The column definitions, including the data types and number of columns, must match the data in the external files.
- DATA_SOURCE = external_data_source_name
Specifies the name of the external data source that contains the location of the external data.
After running the DDL statements, you can access the remote table Db2Table as though it were a local table.
So, now if we want to fetch customers whose country is Greece the query would be executed successfully:
SELECT db1.CustomerId, db1.CustomerName FROM DB1.dbo.Db1Table db1 INNER JOIN DB1.dbo.Db2Table db2 ON db1.CustomerId = db2.CustomerId WHERE db2.Country = 'Greece'; -- Result -- CustomerId | CustomerName ------------------------- 3 ccccccc
Execution Plan
Executing this query -even though it is simple- can be very slow based on the pricing tier your databases are. From the execution plan you may see that most of the time is spent to the remote query execution:
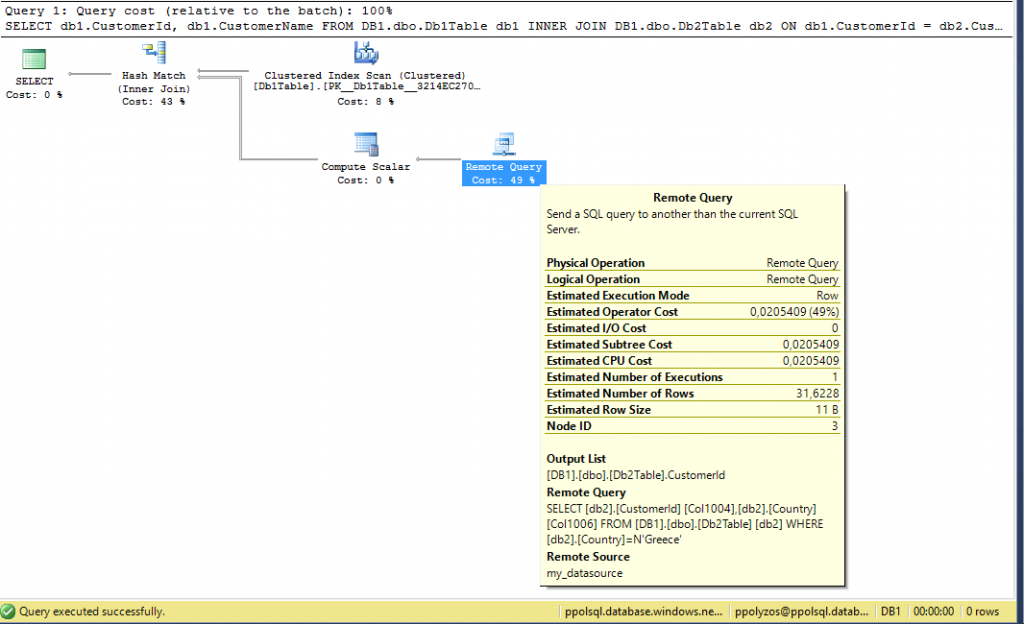
Hi,
Could you please advise if it possible to do elastic queries between Azure and on prem SQL.
Company works from Azure, there is external data needed from a 3rd party company with on prem SQL2016.
Short answer is, yes, you can have your on-premise database as external data source and your on-premise table as your external table.
Although I am not a database specialist, you have to consider the performance impact that a connection between multiple db servers in different environments may have.
Security is another important factor to consider in this case, as you should pay extra attention on connecting your dbs.
Thank you.
I’ve got everything set up, but I get this error:
Error retrieving data from one or more shards. The underlying error message received was: ‘A network-related or instance-specific error occurred while establishing a connection to SQL Server. The server was not found or was not accessible. Verify that the instance name is correct and that SQL Server is configured to allow remote connections. (provider: Named Pipes Provider, error: 40 – Could not open a connection to SQL Server)’.
When I select a top 0 * the query works, shows all the columns. select top 1 * gives the error.
I’ll keep that in mind, we are doing a proof of concept for now.
Most articles / forum posts I find work from querying on querying azure from on prem…
This error usually occurs either when your firewall is not setup properly or remote connections aren’t allowed to your database.
This post might help you.
What pricing tier are using for your Azure SQL database?
Does an elastic database query require that I first convert my database to an elastic azure database?
No you don’t have to convert your database to an elastic azure database. Elastic uery is supported on the Standard and Premium performance tier, howeber the first elastic query can take up to a few minutes on the Standard performance tier, in order to load the elastic query functionality.
SCOPED CREDENTIAL has to be your database credential which you used normally to connect your database